  What's New! Detailed Sitemap All images © by Roberto Piperno, owner of the domain. Write to romapip@quipo.it. Text edited by Rosamie Moore. Page revised in August 2015. |
  The Golden Century: II - The Age of Suleyman The Golden Century: II - The Age of Suleyman
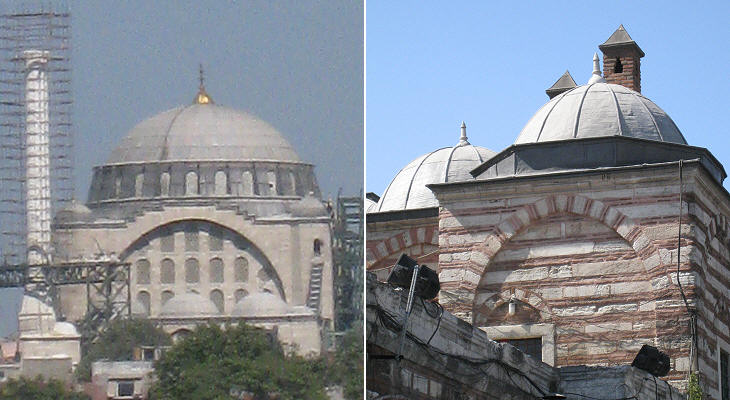
You may wish to see an introductory page to this section first. Suleymaniye Kulliye, the most imposing Ottoman monument of Constantinople was built between 1550 and 1557 by Sultan Suleyman. It was preceded and followed by the construction of many other buildings commissioned by members of his entourage: his wife Haseki Hurrem, his daughter Mihrimah, grand viziers, admirals and chief officers. We should promote family values is a phrase which has become popular in recent years to support the concept that the family is the basic unit of a civilized society. Maybe the air of Constantinople had some special components because family values were quite different from those many attach to this concept. Emperor Constantine killed his wife and his son; Byzantine emperors had a penchant for blinding their fathers, brothers and heirs; Sultan Selim executed his brothers and their offspring. The long reign of Suleyman was no exception to this tradition; the description of the monuments built during this period necessarily makes reference to the treachery and cruelty which characterized this "golden age".
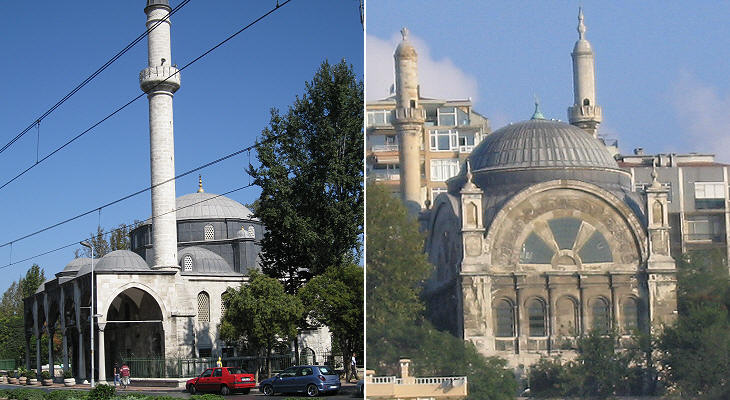
Sinanuddin Yusuf Pacha or abbreviated to Sinan Pacha was appointed Chief Admiral, although he was not familiar with making war at sea; he was however the brother of Grand Vizier Rustem Pacha, husband of Mihrimah, daughter of Suleyman. The actual command of the fleet was entrusted to Turgut Reis, a very experienced assistant of Hayreddin Barbarossa. Sinan Pacha, perhaps to gain the favour of his sailors, commissioned Mimar Sinan (the chief architect at the Sultan's court) a mosque near that admiral's turbe, as if to establish a link between himself and that popular hero. Sinan Pacha was aware that his career was due to his brother and his sister-in-law and he left them his fortune, at a time (end of 1553) they needed it, because their lucky star was temporarily obscured.
In 1553 Sultan Suleyman had four adult sons; Mustafa was the eldest one and the apparent heir as he had been appointed governor of Amasya; his mother was Gulbahar (Rose of Spring) Sultan, a concubine Suleyman had been very fond of before knowing and marrying Roxelana/Haseki Hurrem. The latter with the help of her daughter Mihrimah and of her son-in-law Grand Vizier Rustem Pacha manoeuvred to convince Suleyman that Mustafa was planning to oust him from power. While preparing a campaign against Persia Suleyman summoned Mustafa to his camp near Eregli; once the prince entered the tent he was assaulted by the guards and killed before his father's eyes. There were revolts at Amasya and in other parts of Anatolia; the soldiers regarded the execution of Mustafa as unfair; Suleyman was forced to dismiss Rustem Pacha and to appoint a new Grand Vizier; his choice fell on Kara Ahmet Pacha, husband of the Sultan' sister Fatma, who was highly respected by the army.
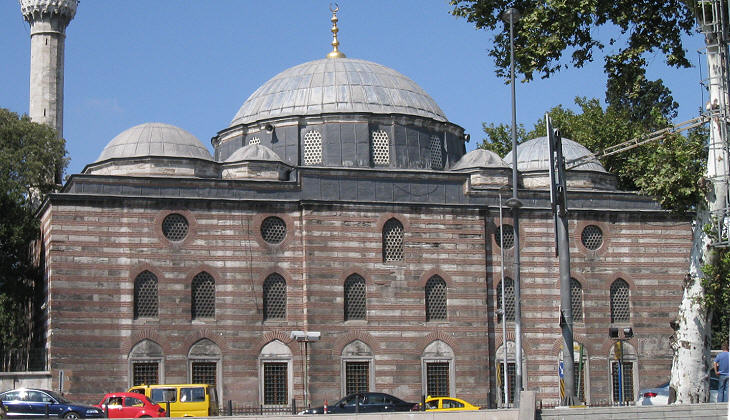
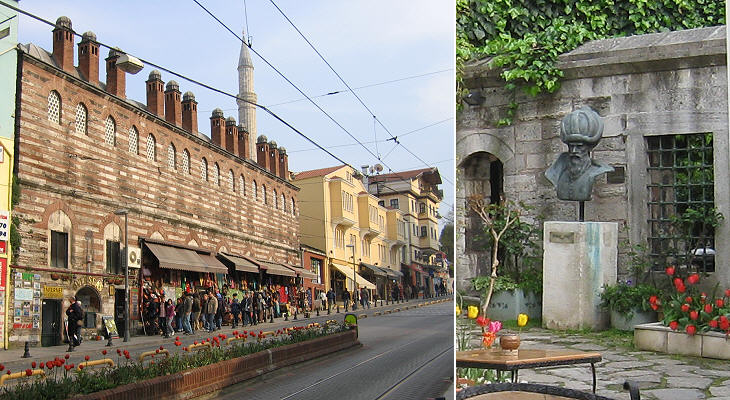
Kara means "black/dark", probably a reference to Ahmet's complexion, but also "unlucky" and that too applies to Ahmet, because he was executed less than two years after having been appointed Grand Vizier; the trio, Haseki Hurrem, Mihrimah and Rustem Pacha, managed to persuade Suleyman that Ahmet was responsible for some wrongdoings in the administration of Egypt; the Grand Vizier did not see the completion of the large complex he had commissioned Sinan. The complex is situated near Top Kapi and it has a very large courtyard surrounded by medrese cells.
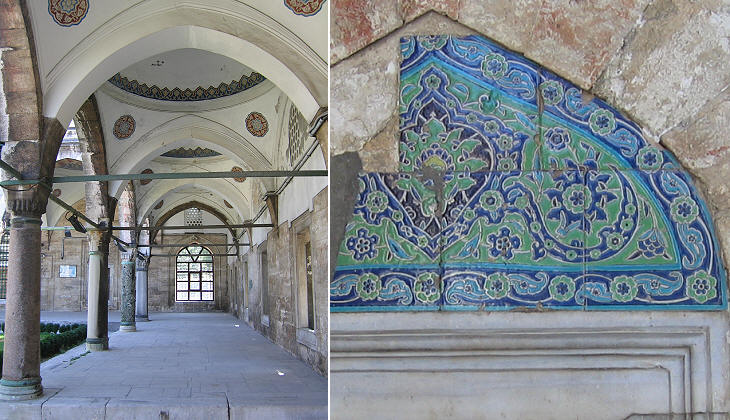
The porch is decorated with ancient columns and tiles known as "cuerda seca" (literally dry cord); this is a Spanish term used to design a procedure for making tiles which was introduced by the Arabs: it is characterized by lines of special manganese paint. These partition the tile surface to prevent glazes of different colours from mixing. In Constantinople these tiles can be identified by the presence of green and yellow in addition to the traditional blue colours which prevailed in the Iznik type.
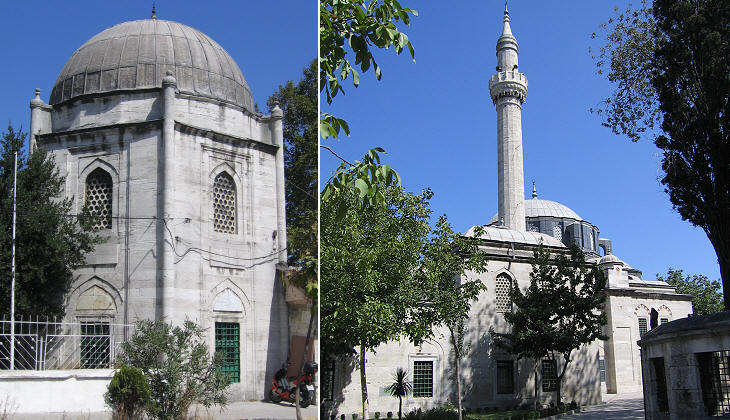
Hadim (eunuch) Ibrahim Pacha never reached the rank of Grand Vizier, but in his capacity of Chief White Eunuch of the Harem, he enjoyed the trust of Suleyman and Haseki Hurrem. Two months after the execution of Mustafa the couple feared that Sehzade Mehmet, Mustafa's six year old son, could be acclaimed sultan by the soldiers loyal to his father. Hadim Ibrahim Pacha was sent to Bursa (where Mustafa had been laid to rest) to personally strangle Sehzade Mehmet.
In 1551 Hadim Ibrahim Pacha commissioned Mimar Sinan a small kulliye near Silivri Kapi on the Seventh Hill. It included a hammam and a mektep, an elementary school, which are lost. The location of this complex in a neighbourhood where the population was predominantly Christian, shows his desire to promote Islam. Today the mosque is surrounded by a small cemetery and, being built on slightly higher ground, it has a very evocative aspect.
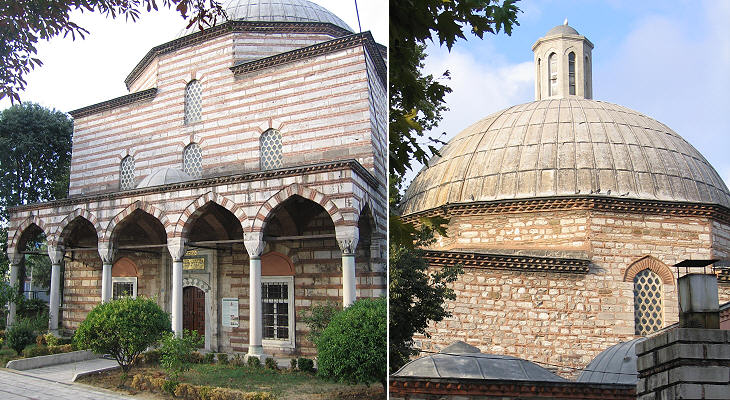
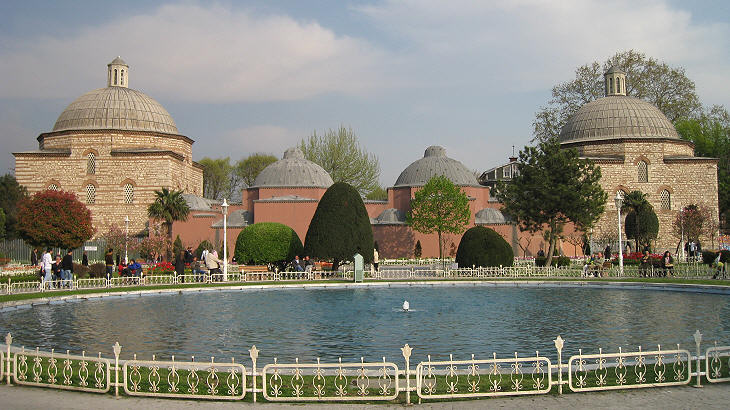
Haseki Hurrem commissioned Sinan the construction of a hammam near Hagia Sophia; it is a very elegant building which was completed just before her death in 1558. She had ensured Suleyman's heir would be one of his sons, but at the time of her death Suleyman had not yet made his final choice.
Some think that in the Muslim world women are not regarded as equal to men; they might change their opinion after seeing this work by Mimar Sinan (the two domes are not identical because perfect symmetry should be reserved to God).
Mimar Sinan was not only a great architect, but also a man with many diplomatic skills; due to his position he was very close to Suleyman and his entourage, but he managed not to be associated too strictly with any member of the family or key officer.
Even a finely designed building loses its interest when it is too much adapted to the needs of business. In 1559 Sinan designed a medrese for Cafer Aga, the Chief Black Eunuch. It is today located along a very commercial street and shops have been opened in its structure; the small courtyard is a crowded café: one wonders what the great architect would say if only he could speak.
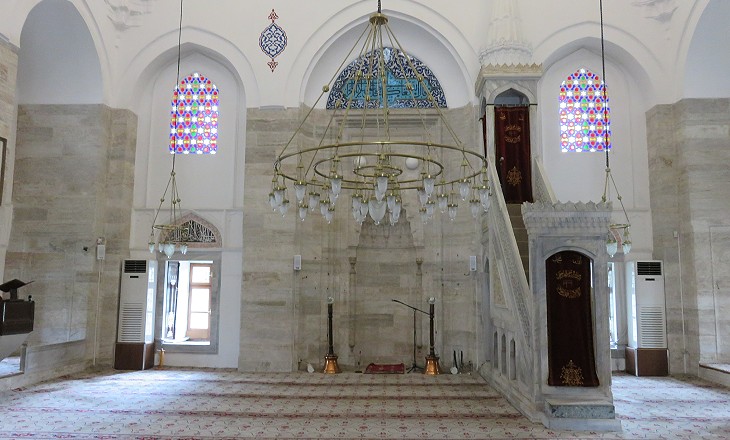
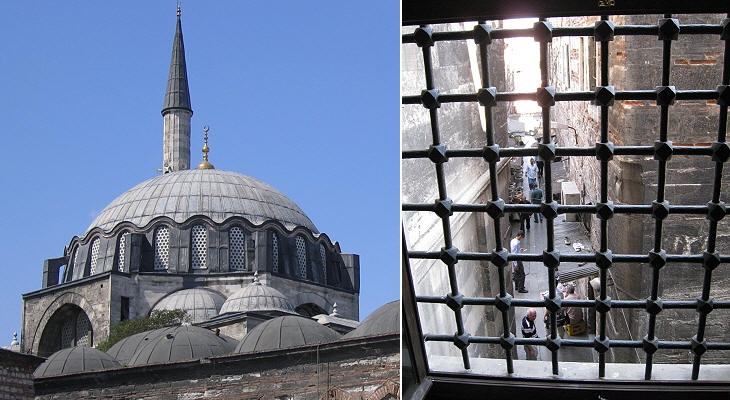
Sinan started working on the kulliye commissioned by Suleyman in 1550; the mosque was completed in 1557; the completion of the complex required a few more years. From its location at the top of the Third Hill, Suleymaniye Kulliye dominated the skyline of Constantinople. When Rustem Pacha, who was again Grand Vizier, decided to commission his own mosque he was careful not to offend Suleyman by building something which could be seen as too imposing for a humble servant of the Sultan. He therefore chose a location at the foot of the Third Hill between this and the Golden Horn. The area was and still is a busy marketplace; Sinan built the mosque on a terrace above a covered bazaar: the rent from the shops was used to maintain the mosque.
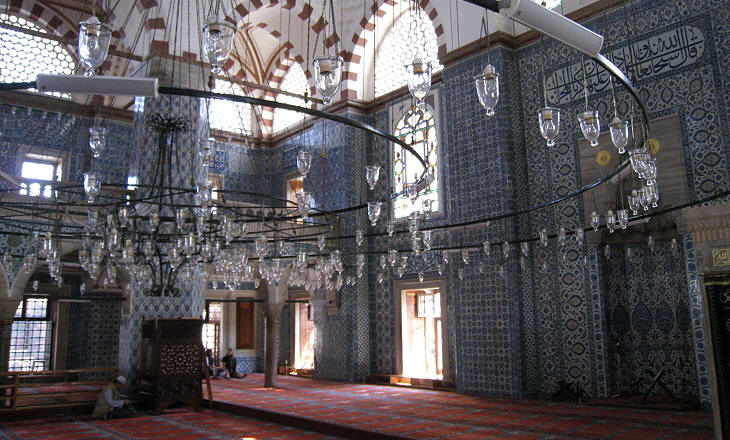
The interior of the mosque is striking; because it is not an extremely large building one can appreciate the tiles which decorate it both in their overall effect and in their details.
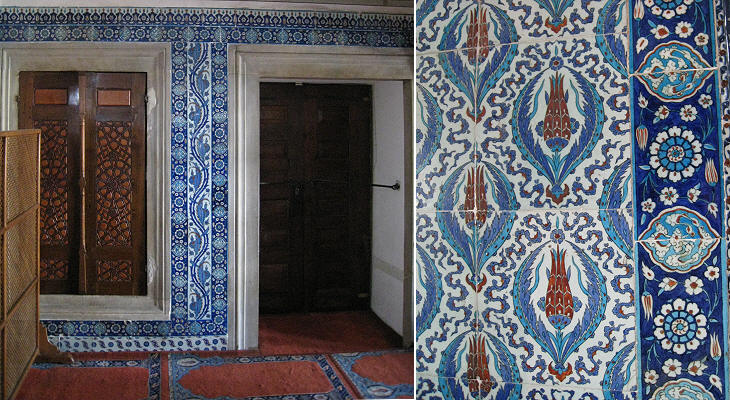
The tiles are characterized by the use of red with the traditional blue; the red came from a type of clay (bole) found in Armenia; for this reason these tiles are called "Armenian boles". The image used as background for this page shows another detail of the tile decoration.
Rustem Pacha died without seeing the completion of his mosque and the end of the fight for the succession between Suleyman's two remaining sons: Selim and Beyazit. In 1559 their rivalry broke out in a civil war and Beyazit sought refuge in Persia.
At the time of the execution of Mustafa, Suleyman had three remaining adult sons: Selim, Cihangir and Beyazit. Cihangir was a hunchback and this prevented him from aspiring to the throne; because of this he had no reasons to hate Mustafa and was very affectionate to him; he died shortly after having learnt about the execution of his stepbrother; according to the traditional account because of the grief caused by that event. Suleyman commissioned a mosque to celebrate him; it was rather small and in a peripheral location (a hill overlooking the Bosporus); the original mosque was designed by Sinan, but the current building is modern. Today Cihangir is the name given to the neighbourhood surrounding the mosque; it is widely known for having been described in his novels by Orhan Pamuk, 2006 Nobel Prize in Literature. Not very far from Cihangir Camii, but on the Bosporus shore, Sinan built another mosque for Mehmet, a Kadiasker (kadi=chief asker=soldier) who is however better known as a poet/savant: the building is called Molla Celebi Camii; Molla means mullah and also high-ranking kadi; Celebi means prince and is a generic title of respect. Today the mosque suffers from being next to a very busy road.
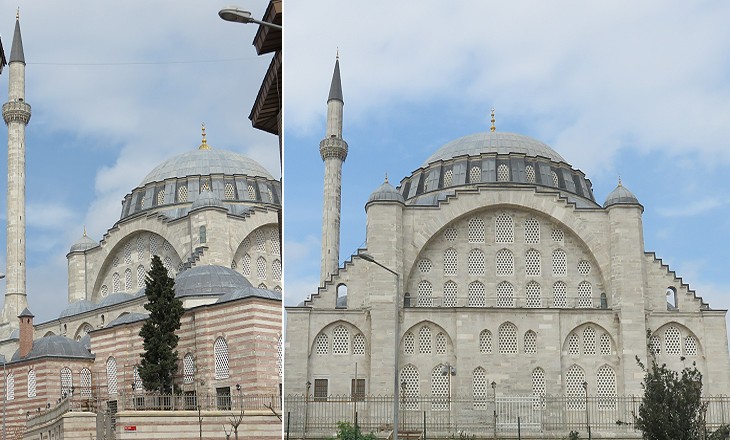
Mihrimah supported Selim as heir to Suleyman; he was the least capable of her brothers and was known for being a drunkard and for lacking leadership skills; probably she supported him exactly for this reason. In 1561 Suleyman convinced the Persian Shah to execute Beyazit and his four sons. The unlucky prince had a fifth son he had not brought with him; by order of Suleyman this child (aged three) was also executed. Mihrimah enjoyed her father's trust until he died in 1566 and then she retained a great influence over her brother Sultan Selim II. In 1565 she commissioned Sinan a mosque at Edirne Kapi. It was the second mosque the great architect built for the princess because one of his first works was Mihrimah Camii at Uskudar.
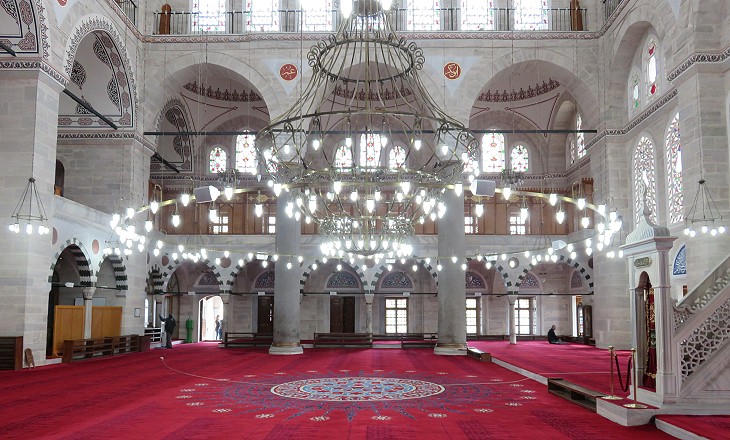
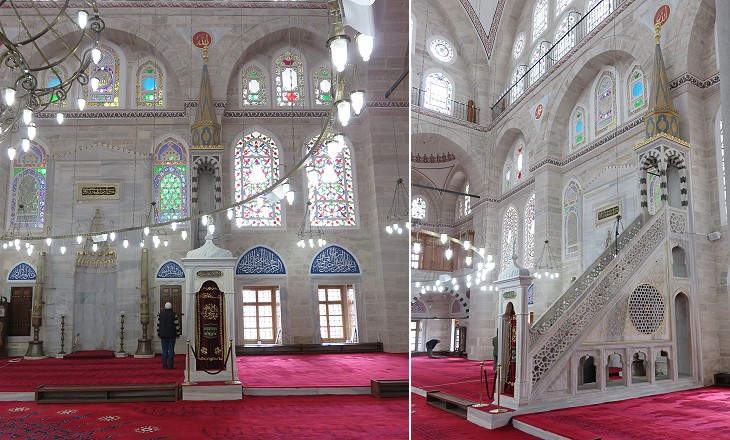
Sinan experimented with a new design which allowed for large windows. Its positive effects are immediately visible when visiting the interior.
The mosque has been extensively refurbished as part of a massive plan promoted by the government. This decision has been dubbed as Neo-Ottoman and in contrast with the secularist principles introduced by Mustafa Kemal Ataturk in the 1920s.
Introduction to this section Roman Memories Hagia Sophia Byzantine Heritage (before 1204) Hagia Irene and Little Hagia Sophia Roman/Byzantine exhibits at the Archaeological Museum Great Palace Mosaic Museum St. Saviour in Chora Byzantine Heritage (between 1204 and 1453) First Ottoman Buildings The Golden Century: I - from Sultan Selim to Sinan's Early Works The Golden Century: III - Suleymaniye Kulliye The Golden Century: IV - Sinan's Last Works The Heirs of Sinan Towards the Tulip Era Baroque Istanbul The End of the Ottoman Empire Topkapi Sarayi Museums near Topkapi Sarayi The Princes' Islands Map of Istanbul Other sections dealing with Constantinople/Istanbul: The Walls of Nova Roma Galata Clickable Map of Turkey showing all the locations covered in this website (opens in another window). |


















