  What's New! Detailed Sitemap All images © by Roberto Piperno, owner of the domain. Write to romapip@quipo.it. Text edited by Rosamie Moore. Page added in May 2012. |
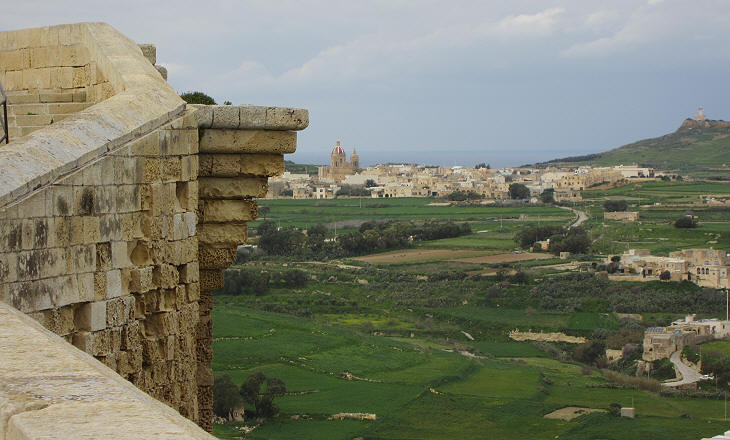
 - Victoria (Rabat) in the Island of Gozo - Victoria (Rabat) in the Island of Gozo(detail of a statue of St. Catherine of the Wheel in the parish church of Zejtun) Gozo (26 sq. mi.) is the second largest of the Maltese Islands and it lies to the north-west of Malta. There is evidence that it was inhabited in prehistoric times. In general its history is strictly linked to that of Malta.
Notwithstanding the small size of the island, inscriptions indicate that during the Roman Empire, the main settlement of Gozo had the status of municipium and had formally elected magistrates. The Roman town was located around a small hill which enjoyed a commanding view over the whole island. How Gozo could house a municipium can only be explained with Pax Romana, the long period of peace and stability experienced by the Roman Empire which began at the end of the civil war between Octavian and Antony in 29 BC and lasted until the death of Emperor Marcus Aurelius in 180 AD. The Mediterranean Sea was free from piracy and this favoured the development of trade on an unprecedented scale. Malta and Gozo were renowned for their honey and their prosperity was based on this trade.
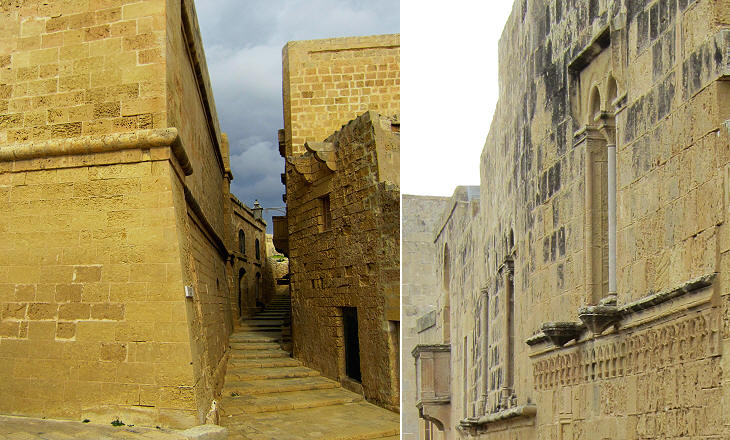
The fall of the Roman Empire exposed Gozo to being raided by pirates. The Arabs tried to protect the inhabitants by fortifying the hill of the Roman town which was renamed Rabat, which in Arabic indicates a fortified location. The Normans and after them the Spaniards maintained and strengthened the fortifications of Rabat.
In 1530 Gozo was assigned to the Knights Hospitallers who did not care much about this island which did not have any natural harbours. In 1551 Ottoman corsair Dragut landed on Gozo and took Rabat. He was not interested in permanently occupying the island and therefore he carried all its inhabitants away as slaves, something which was a blow to the Knights' reputation as defenders of Christians. Only after the 1565 Great Siege of Malta which the Ottomans were forced to lift, the Grand Masters dedicated themselves to repopulating and to protecting Gozo.
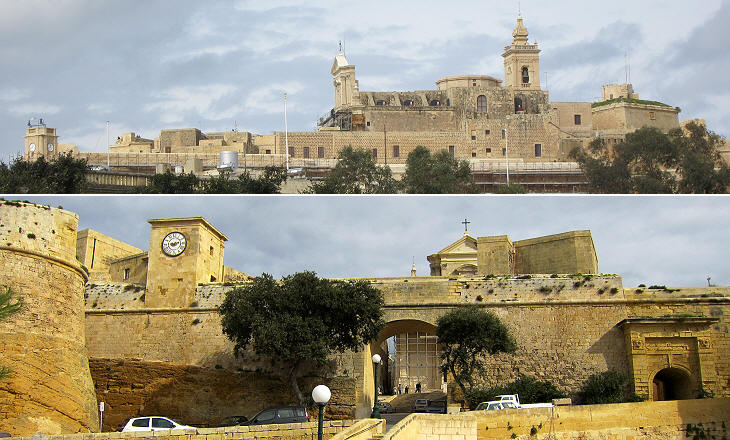
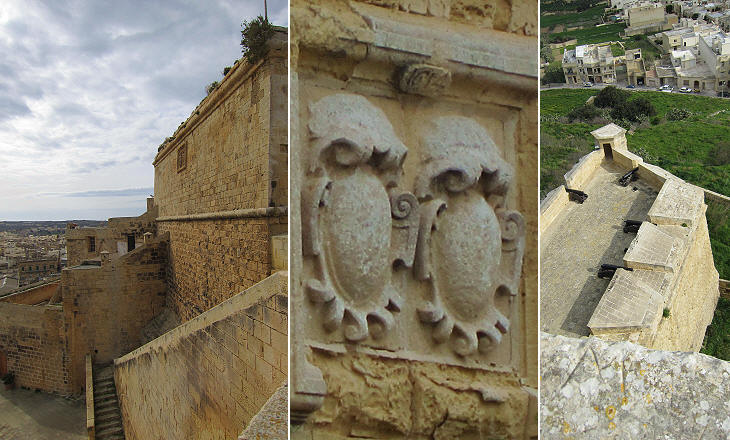
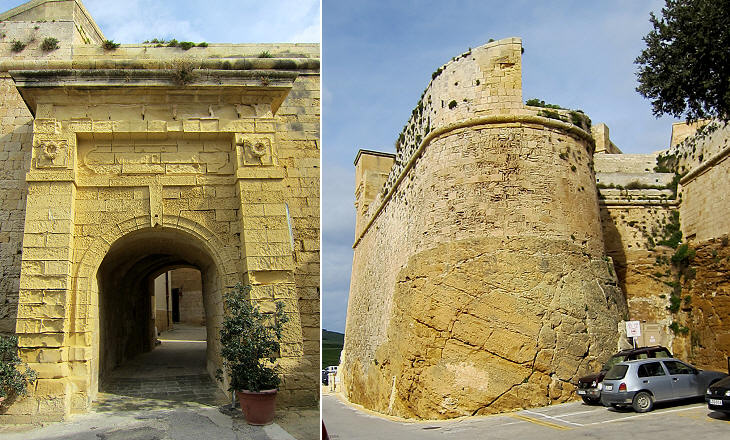
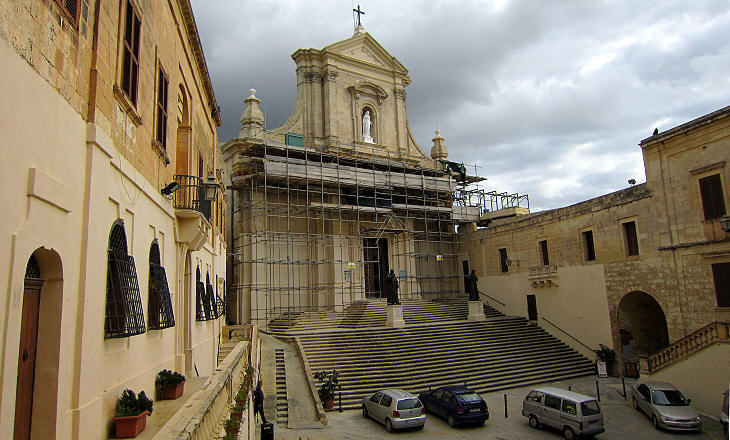
The reconstruction of the Citadel of Rabat was promoted by Grand Masters Garzes and Alof de Wignacourt. Its new fortifications proved effective in preventing new Ottoman attacks and they were not greatly affected by the earthquake which struck the island in 1693.
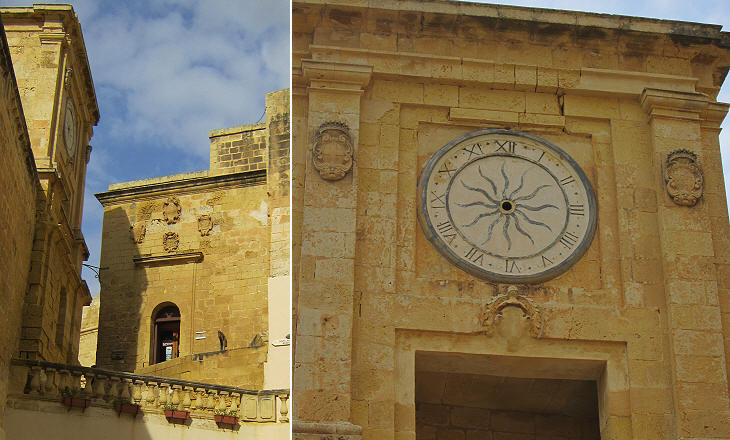
In 1956 a large opening in the walls of the Citadel allowed easy access to its main square, but prior to then the Citadel had only one gate which was protected by two bastions one of which shows how the natural rock of the hill was cut to adapt it to defence needs.
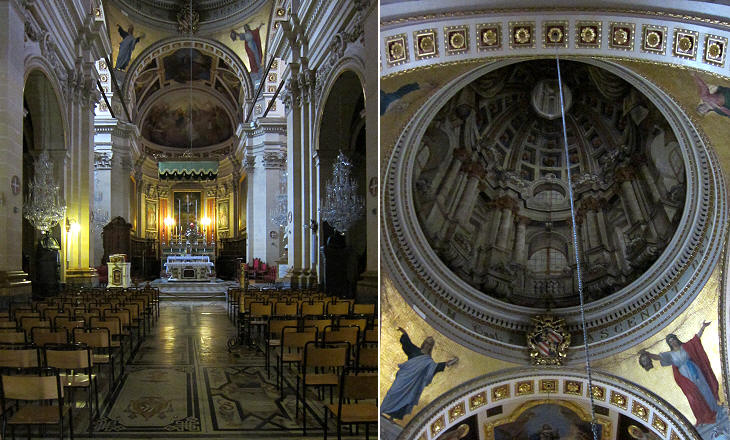
The 1693 earthquake greatly damaged the church of the Citadel, similar to what occurred to the cathedral of Cittą Vecchia (Mdina). The two churches were rebuilt by Lawrence Gafą, who at Rabat designed a neat faēade without the couple of bell towers which characterize many Maltese churches. The two modern bronze statues in front of the faēade portray Pope Pius IX, who in 1864 approved a separate diocese for Gozo, and Pope John Paul II, who visited the island in 1990.
The Citadel is very small and as it was almost entirely occupied by public buildings, the large majority of the population of Rabat lived outside its walls. The Grand Masters placed many coats of arms on the facilities they built inside the Citadel, but almost all of them were erased during the French occupation in 1798-1800.
According to the design of Lawrence Gafą the church was to be completed with a dome, but this was never actually built. In 1739 Antonio Manuele from Messina in Sicily painted an illusionary dome, similar to that of S. Ignazio in Rome. The coat of arms of Pope Pius IX was added when the church became a cathedral.
A 1903 directory of factories in Rome lists Fabbrica di Statue Religiose Zanazio Rosa & C. in Borgo as employing 37 workers and three children in the manufacturing of painted gypsum statues which were sold throughout Italy and in countries where Italians had migrated such as Argentina. You may wish to visit the website of the current owners of the brand with images of the old workshop (external link).
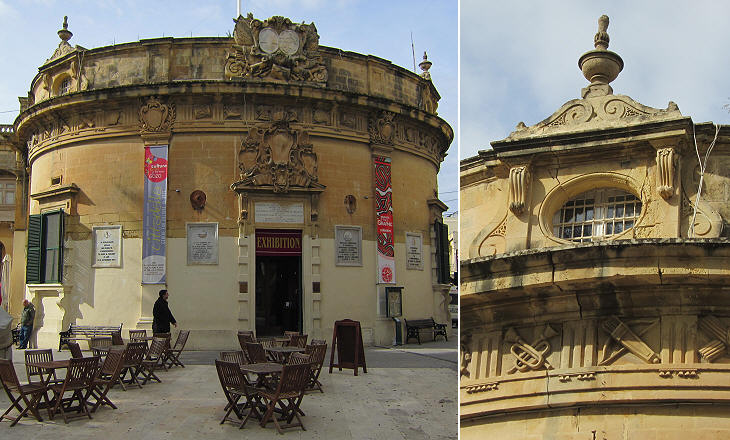
Banca Giuratale is located outside the Citadel and it was designed in 1723 by Charles de Mondion for Grand Master Vilhena. The building served several purposes including that of housing the meetings of the giurati, members of a sort of city council having very limited powers. Rabat was renamed Victoria in 1897 to celebrate the Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria.
The image used as background for this page shows a 1529 coat of arms of Bernardo de Opuo of Gozo who slightly modified the Latin saying Fortuna audaces iuvat (Fortune favours the bold) (in the Archaeological Museum). Move to: Introductory Page Brief outline of the history of Malta before 1530 The Grand Masters of the XVIth century The Grand Masters of the XVIIth century The Grand Masters of the XVIIIth century Valletta: the fortifications Valletta: the churches Valletta: other monuments Borgo/Cittą Vittoriosa (Birgu) Senglea (Isla) Cittą Cospicua (Bormla) Floriana Other Fortifications Cittą Vecchia (Mdina) Churches in the minor towns Other monuments in the minor towns Rome and Malta     |










